Acute Stroke Services
At John Muir Health, our acute stroke services are driven by our motto, “TIME IS BRAIN” – where every second counts and prompt treatment can save a life or reduce permanent disability. Our team of specially trained practitioners and staff are available 24/7 to rapidly identify and treat patients with the most current techniques and advanced technology.
Stroke Diagnosis
When a patient arrives to the emergency room with symptoms of a stroke, our care team is focused on rapid and accurate diagnosis of the type of stroke and severity. Our clinicians use advanced neuro-imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) imaging to diagnose stroke. Other tests that may be used to diagnose stroke and to evaluate its effects on brain function include:
- Tests to evaluate electrical activity in the brain, such as electroencephalography (EEG) and evoked potentials
- Tests to assess blood flow in the brain, including CT and MR angiography and perfusion, sonography, ocular plethysmography, and digital subtraction angiography
- Radionuclide angiography
- Functional MRI
- Artificial intelligence technology that aides in early detection, accurate diagnosis, and timely treatment.
Stroke Treatment
Stroke treatment is dependent on the type of stroke.
Ischemic Stroke Treatment
The treatment for ischemic stroke is clot removal. Doctors can accomplish this with medication and mechanical treatments:
- Clot-dissolving Drugs
- Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is the most common emergency stroke treatment medication. tPA dissolves arterial blood clots that block nourishment from getting to the brain. This life-saving medication is delivered intravenously to ischemic stroke patients within 4.5 hours of a stroke.
- Many people don’t arrive at the hospital in time to receive the medication, which can save lives and reduce long-term effects of stroke. So it’s important to identify stroke and seek treatment immediately.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy
- If there is a large clot that tPA is unable to dissolve or when tPA is not indicated, our Neurointerventional providers may perform mechanical thrombectomy on patients who meet eligibility criteria. In this procedure, doctors use a wire-cage device called a stent retriever. They thread a catheter through an artery in the groin up to the blocked artery in the brain. The stent opens and grabs the clot. Special suction tubes may also remove the clot.
- Mechanical thrombectomy can be performed up to 24 hours after a stroke. It’s important to identify stroke and seek treatment immediately to have the best chance at reducing permanent disability.
Hemorrhagic Stroke Treatment
The treatment for hemorrhagic stroke is to stop bleeding from ruptured blood vessels. Our specialists treat hemorrhagic stroke patients with the most technically advanced treatments available:
- Endovascular procedures. Endovascular procedures may be used to treat certain hemorrhagic strokes. The doctor inserts a long tube through a major artery in the leg or arm and then guides the tube to the site of the weak spot or break in a blood vessel. The tube is then used to install a device, such as a coil, to repair the damage or prevent bleeding.
- Surgical treatment. Hemorrhagic strokes may be treated with surgery. If the bleeding is caused by a ruptured aneurysm, a metal clip may be put in place to stop the blood loss.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; American Stroke Association
John Muir Health 2024 Quality Report Card: Comprehensive Stroke Center
| Measure | Description | Our Result | Other California Hospitals | Other Certified Comprehensive Stroke Centers |
John Muir Health Rating
|
| Door to Needle |
Average time from arrival at our facility to the administration of thrombolytic treatment | 34 minutes | 37 minutes |
34 minutes |
Same or Better |
| Symptomatic Bleed Rate (IV) |
Rate of bleeding in the brain after IV thrombolytic treatment | 6.5% | 3.0% | 2.30% | Worse |
| Door to Groin |
Average time from arrival to skin puncture for mechanical thrombectomy | 24 minutes | 69 minutes |
62 minutes |
Better |
| Substantial Reperfusion Rate | Percent of patients that achieve full reperfusion (vessel completely open) with mechanical thrombectomy | 89.70% | 88.00% | 86.60% | Better |
| Symptomatic Bleed Rate (IR) | Rate of bleeding in the brain after thrombectomy | 4.5% | 8% | 5.90% | Better |
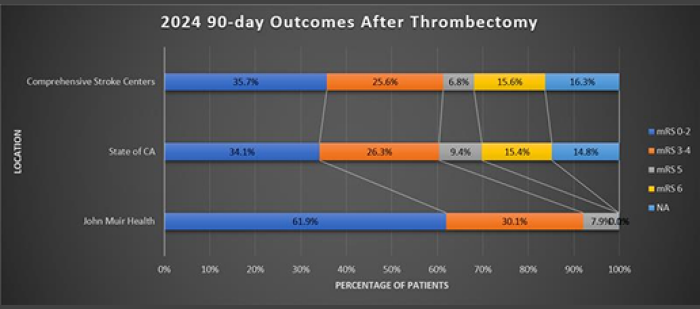
| Legend | |
| mRS 0-2 | Independent (bathing, dressing, walking) |
| mRS 3-4 |
Needs some help (walker, cane, family) |
| mRS 5 |
Bedridden |
| mRS 6 | Deceased |
Meet Our Team
At John Muir Health our goal when treating stroke patients is to preserve our patient’s quality of life. That is why we have assembled a comprehensive and experienced team of specialists - neurologists, neurosurgeons, neurocritical care specialists, and nurses - onsite 24/7 who work together as a team to care for our stroke patients.
To ensure our program meets the highest standards, our acute stroke program administrative team ensures we follow all established clinical practice guidelines and have access to the latest lifesaving technologies and procedures.
Stroke Program Administrative Team
Jennifer Cave-Brown, MS, RN, NP, ACNP-BC, CNRN
Stroke Program Coordinator and Nurse Practitioner
Susan Green, MS, RN, CNS, CNRN
Stroke Clinical Nurse Specialist
Deanna Burghardt, RN
Stroke Nurse Navigator
Shaheen Sohi, RN, CCRN
Stroke Nurse Navigator
Christian Swinney, MD - Neurologist
Stroke Program Medical Director
Ira Finch, MD - Neuro-interventional Radiologist
Maxwell Merkow, MD - Neurosurgeon
Neurosurgery Medical Director
Moussa Yazbeck, MD - Neurocritical Care Intensivist
Stroke Resources
Stroke Prevention
BE FAST - Stroke Signs
For more information, email us